INTRODUCTION:
Johnson & Wales University developed plans for its Center for Physician Assistant Health Sciences School – a first-of-its-kind facility in Rhode Island. Plans called for an 18,000 square foot facility developed through renovations and modernization of an existing two-story building and addition to the structure. Design loads were up to 150 kips for columns and 35 kips/foot on exterior walls. The facility houses lecture halls, active learning classrooms, labs and study spaces.
Geotechnical Conditions:
The project was challenged by difficult soil conditions including loose sand and silt urban FILL with construction debris up to 11 ft thick underlain by up to 6 feet of PEAT. More competent soils including medium dense to dense outwash SAND and SILT were then encountered and extended to 58 feet followed by glacial TILL. Groundwater was at 15 feet.
Project Challenges:
Construction of a heavily-loaded building addition adjacent to sensitive existing structure on uncontrolled fill and organics.
Advantages
- Cost savings over traditional deep foundations
- Flexibility of installation from various grades and locations
- High capacity for reduction of scope
- Rapid installation
Design and Construction Solution:
The geotechnical engineer identified a concern for construction of the new building addition on ground consisting of urban fill and organic soils combined with tying into the existing structure supported on shallow spread footings. Original recommendations included a combination of compaction grouting for new construction and helical piles for underpinning of the existing building walls. Ground improvement approaches were also considered but dismissed because of tight access issues and vibrations near the existing structure.
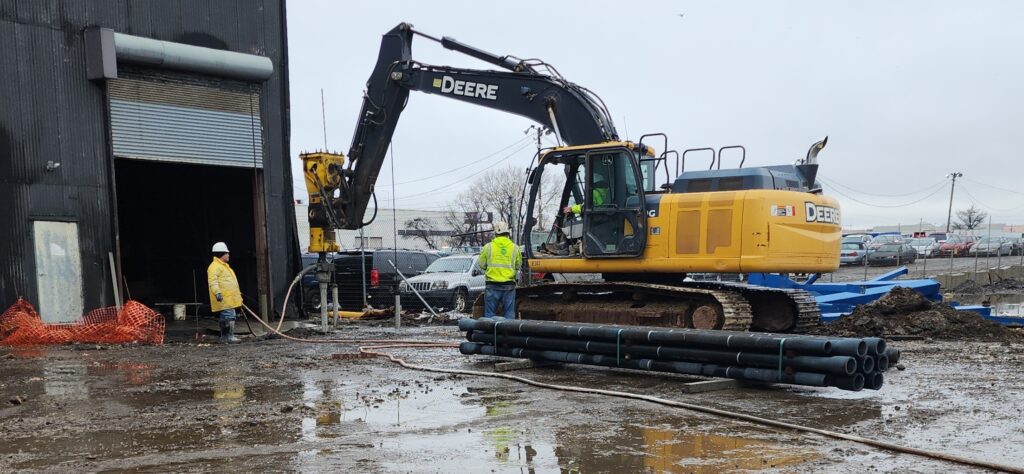
An alternative solution, Helical Drilling, Inc. worked with the geotechnical engineer and project team to design a Ductile Iron Pile (DIP) solution to provide support for the heavily-loaded new building foundations in concert with the planned helical anchors for existing building support where limited head-room restricted access with the on-site DIP installation equipment. DIPs were designed for an allowable capacity of 70 kips using a 118/7.5 series pile. Helical Drilling rapidly installed the ductile iron piles to extend through the fill, peat and outwash sand/silt to terminate in the competent glacial till. Limited borings within the work area combined with a steep slope in the till/bedrock required that the piles be advanced to greater depths at one end of the work area, ranging from 65 to 90 feet. The crew was able to adjust to the increased depth by simply adding two additional extensions of ductile iron pile. The piles were seated into the till or bedrock using the driving set criteria of less than 1 inch of penetration per minute of driving. DIPs were filled with grout during installation to further enhance the structural capacity.
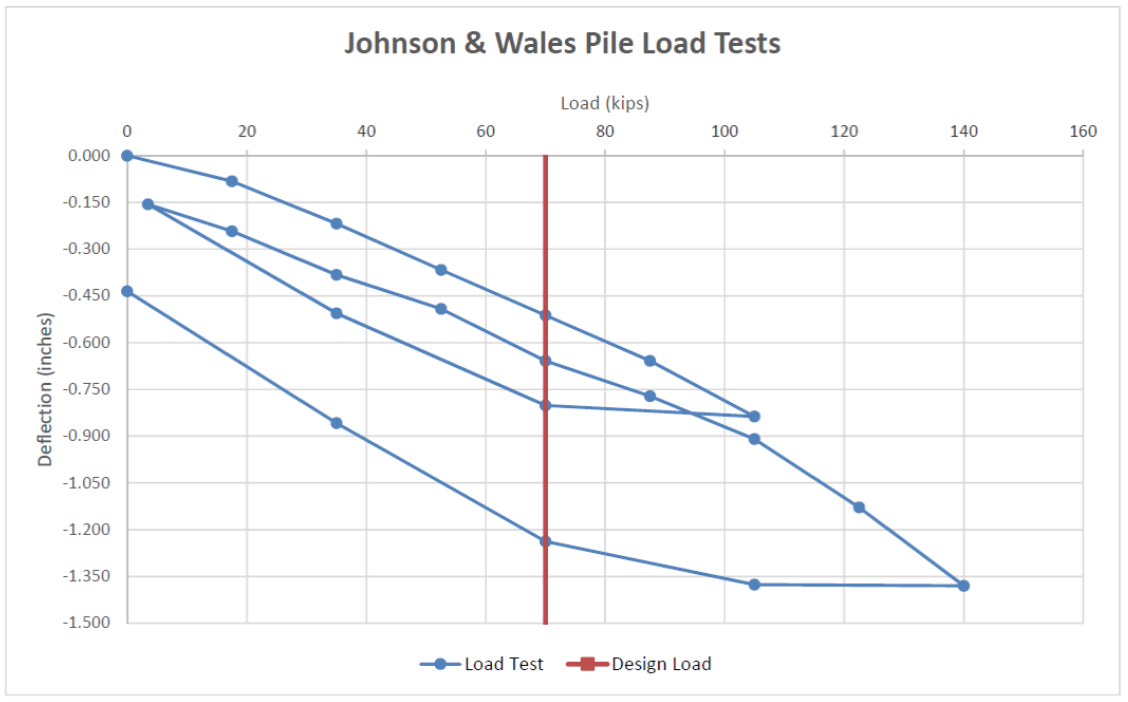
A full-scale load test was performed to confirm the design capacity and performance. At the design load of 70 kips, deformation of the end-bearing DIP was limited to 0.5 inches. The test was performed up to 200% of the design load (140 kips) and confirmed capacities at much higher loads.
Project Team Members
DIP Design/Build Partner: Helical Drilling, Inc.
Geotechnical Engineer: GZA GeoEnvironmental
General Contractor: Shawmut Design & Construction
Structural Engineer: Odeh Engineers, Inc.
Architect: DBVW Architects
Sitework Contractor: Site Tech




