Project Description:
Improvements to the existing buildings at Madison Park Village included construction of a new 1,640 square foot addition. The addition was designed on a pile-supported mat foundation with a total load of 1,300 kips. Nine piles with working capacities of 110 to 190 kips were specified.
Geotechnical Conditions:
A site-specific boring performed encountered variable “urban” fill consisting of sand, gravel and clay along with brick, concrete and asphalt extending to a depth of 28 feet below existing grade. The fill was underlain by soft peat and organic silt to 42 feet followed by very stiff Blue Clay. The clay was underlain by medium dense to dense sand starting at 62 feet and continuing until the maximum explored depth of 106 feet. Groundwater water was encountered at 9 feet below grade.
Project Challenges:
Install low-vibration piles with sufficient capacity in the excavation adjacent to the existing residential buildings.
Advantages
- High capacity friction pile
- Ability to work in limited access area with varying grades
- Low vibration installation adjacent to existing building
Design and Construction Solution:
Structural drawings specified pile capacities of 110 kips and 190 kips at the pile locations but did not identify a specific pile type. The project was ideally-suited for Ductile Iron Piles because of the tight site access, vibration sensitivity and work to be performed at a depressed working level. Helical Drilling, Inc. developed an approach using Ductile Iron Piles with a working capacity of 110 kips. Two piles were planned at the locations of the 190 kip pile loads.
The Ductile Iron Pile system was designed as a friction pile to penetrate the fill and organics and bond in the stiff clay and underlying sand by driving a Series 118/9.0 pile (118 mm diameter with 9.0 mm wall thickness) with a 220 mm oversized conical cap. During installation, sand cement grout was pumped through the pile and out the bottom of the pile to encapsulate the pile in grout within the annular space created by driving the oversized cap. A design length extending into the sand at approximately 22 feet was planned.
A pre-production load test was performed at the site. The test pile was installed 77 feet through the fill and organics to bond in the clay and sand. A telltale was installed at the top of the sand to verify the load transfer to the top of the sand layer. Load test results showed only 0.11 inches of deflection at the design load of 110 kips and 0.46 inches of deflection at 220 kips (200%). Telltale movement at the maximum test load confirmed that 150% of the load was reaching the top of the sand bond zone. Net deflection after unloading was 0.24 inches. Installation of the 13 piles occurred within 2 days. 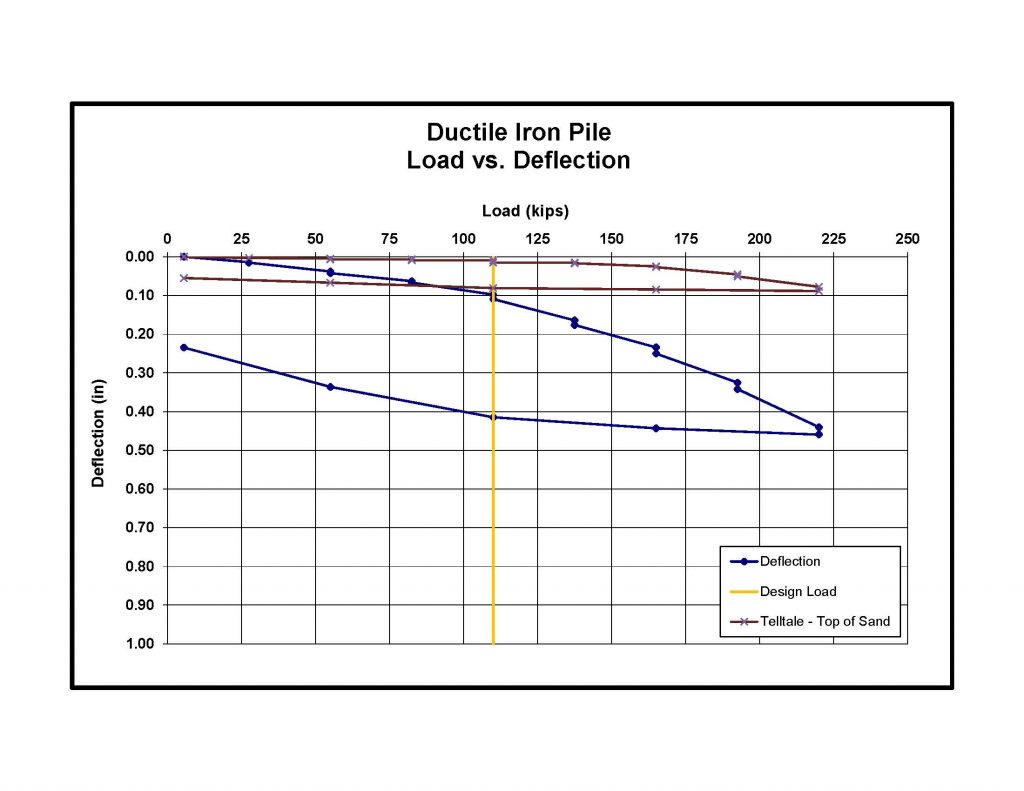
Project Team Members
DIP Design/Build Partner: Helical Drilling
Geotechnical Engineer: Geotechnical Partnership, Inc.
General Contractor: L.D. Russo, Inc.
Architect: Elton & Hampton Architects





